Here we assess the hindcast probabilities of early onset using ACCESS-S2, focusing on an ensemble of 3 hindcast members, that have been calibrated to observations using a quantile-quantile mapping technique to reduce biases. Each hindcast member has been initialised at short intervals and run out for over 7 months, meaning that an onset date is undetermined if 50 mm of rain is not accumulated by the end of the run. For the probability of early onset below (left panel below), we combine 11 different initialisation dates to create a 33-member sample. For example, for Lead month 0, we combine the dates of August 16, 21, 24-31 and September 1. For each year, probabilities are calculated by summing the total number of hindcast ensemble members that show an onset earlier than the observed median (with respect to a smoothed 1960-2018 or 1990-2018 median), and dividing through by the total number of members. For an onset date falling on the median onset date, a 50-50 split is given between an early and late onset. The right panel below shows the observed onset date anomaly referenced against the median onset to judge the performace of the hindcast probability.


The skill of ACCESS-S2's hindcasts of the northern rainfall onset is assessed for each Lead month (i.e., a combination of 11 initialisation dates). The skill is based on the hindcast probabilities that are calculated with respect to a smoothed observed median onset.
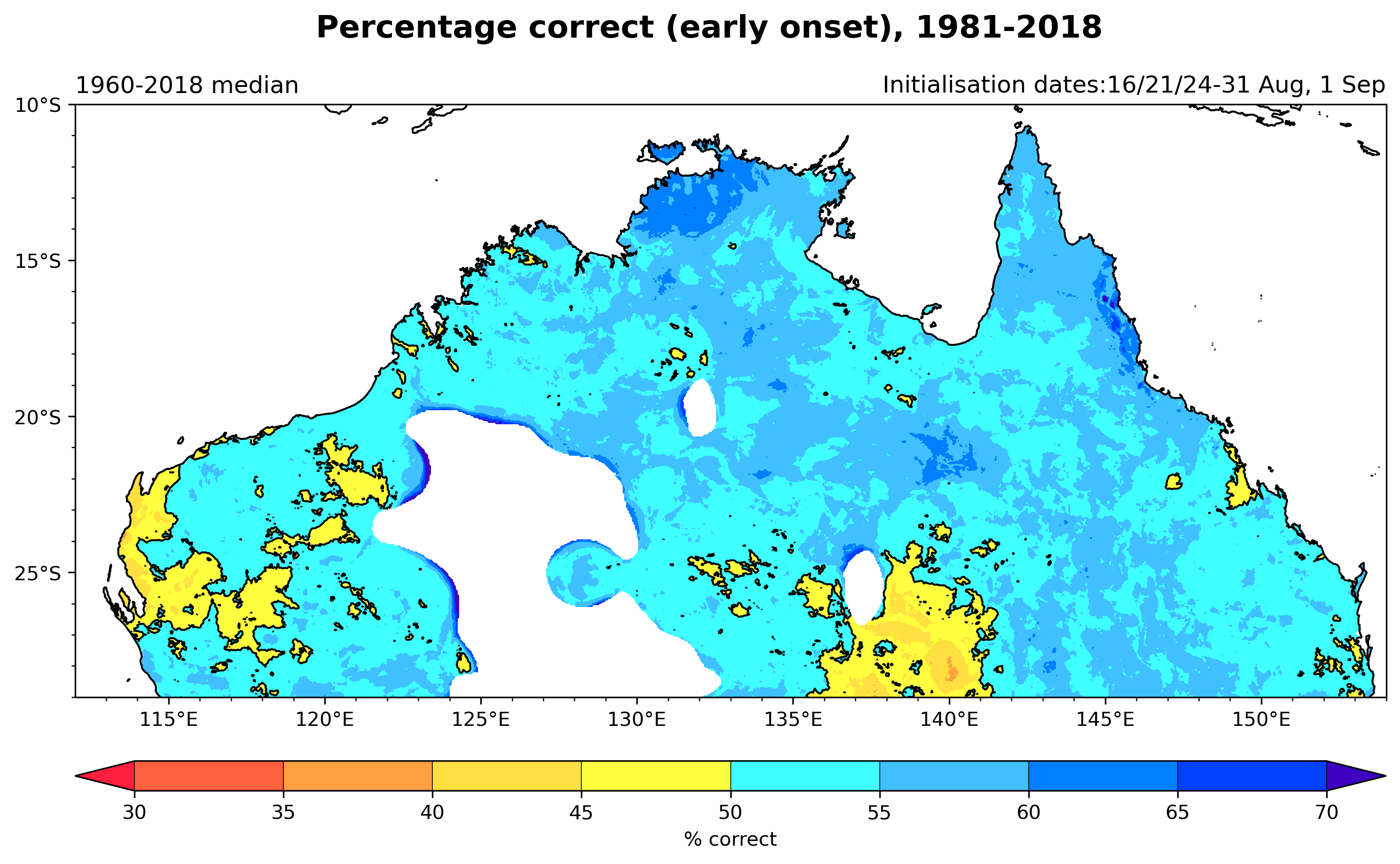
Below, we show the percentage of correct forecasts of early onset over 1981-2018 for each grid point for various lead months, calculated with respect to both a 1960-2018 and 1981-2018 smoothed observed median onset.
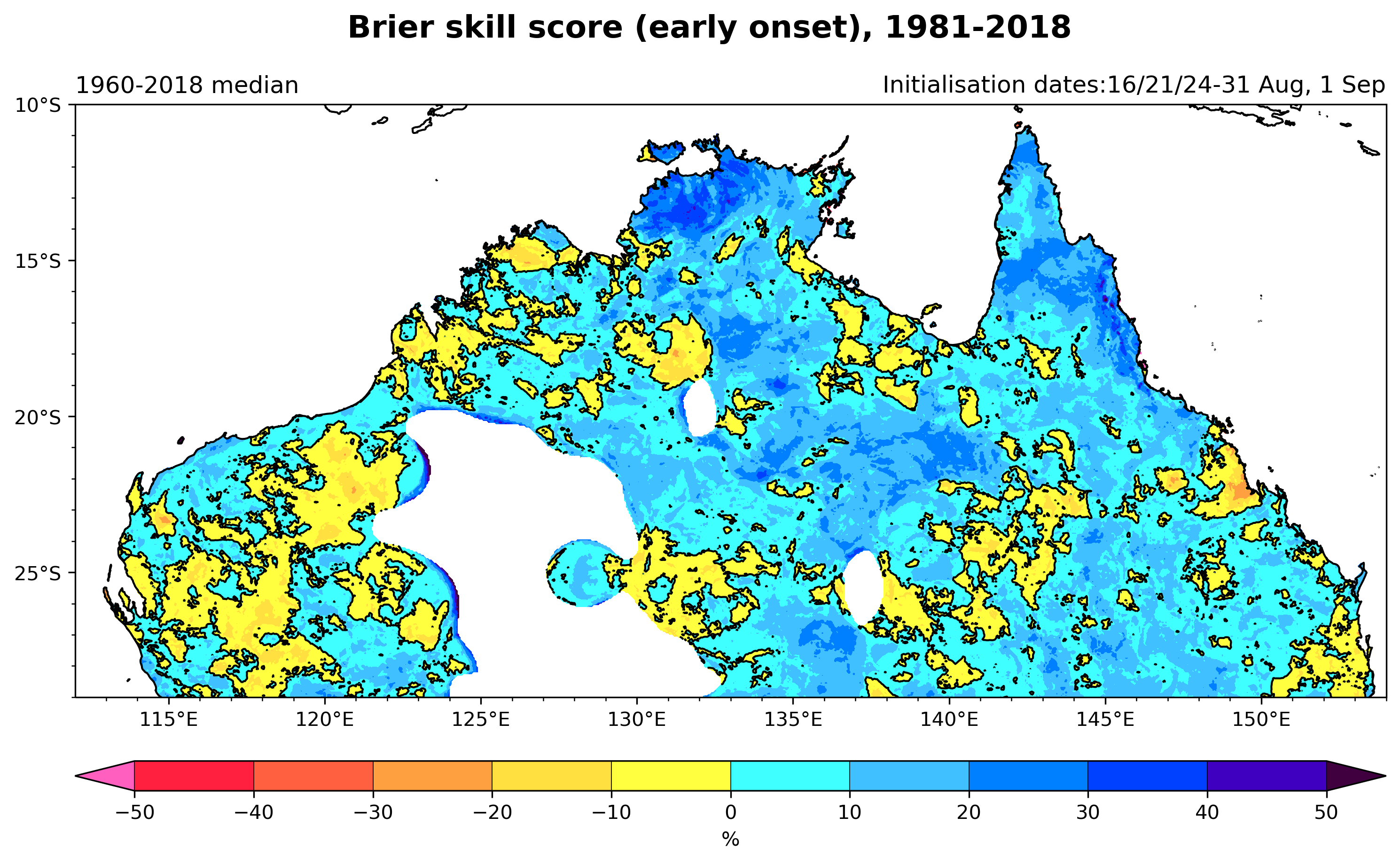
Here we assess the Brier skill score of early onset for each grid point (below left) and the reliability using an attributes diagram for all points north of 29°S (below right).